Incoterms 2022 – 7 conditions apply to all modes of transport

In 11 Incoterms 2022 conditions are used as standards in agreements on transfer of responsibility between buyer and seller, especially in the field of import and export; There are 7 conditions that apply to all methods of transporting goods, including 4 conditions that only apply to river and sea routes. Accordingly, the import and export of goods by air will use a number of Incoterms conditions such as: EXW, FCA, CPT, CIP, DAT, DAP and DDP. As follows:
EXW conditions – Delivered at the factory
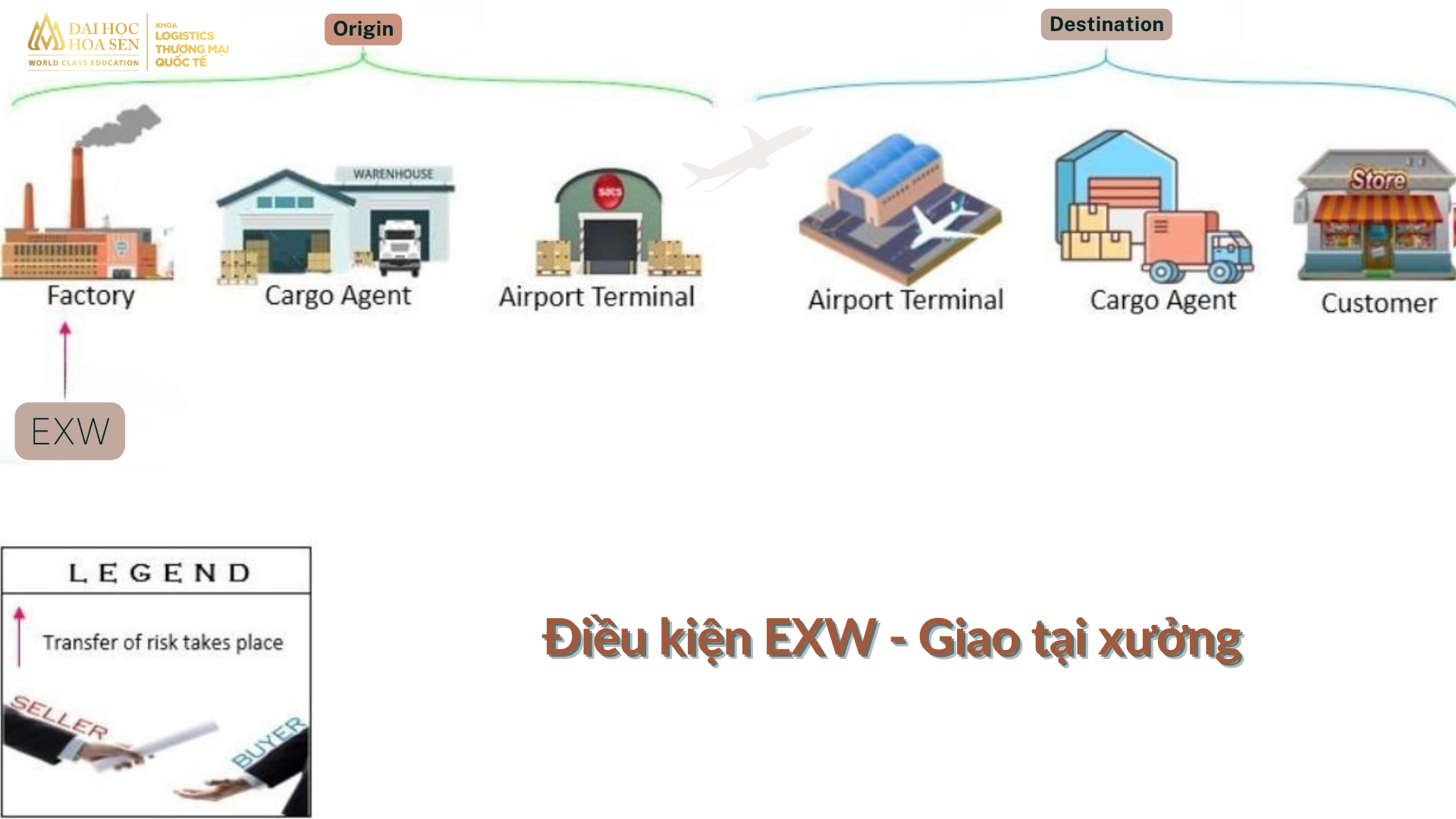
EXW “Ex Works” means that the seller delivers when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer at the seller’s premises or at a named place (e.g. workshop, factory, warehouse, etc.). . The seller does not need to load the goods onto the receiving vehicle and does not need to carry out export customs clearance procedures (if any). The parties should specify as clearly as possible the point at the named place of delivery as the costs and risks to that point are borne by the seller.
The buyer bears all costs and risks involved in taking delivery of the goods from the named point, if any, at the named place of delivery. The remaining tasks will be the responsibility of the buyer, including loading goods onto the vehicle, booking seats on the plane and transporting the goods to their warehouse.
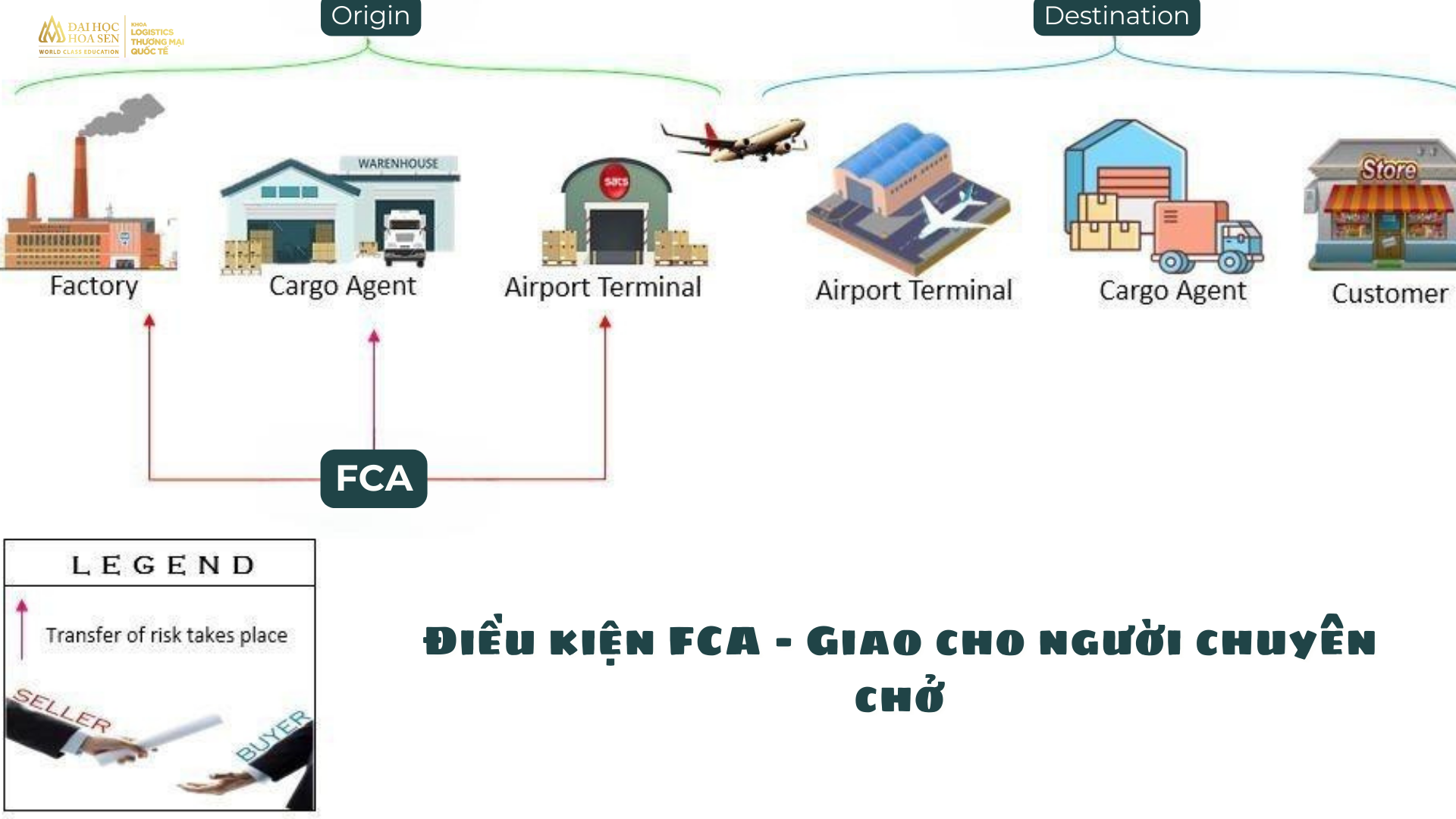
FCA Conditions – Delivered to the carrier
When applying FCA conditions, the seller will have to deliver and load the goods onto the buyer’s means of transport waiting at the warehouse or factory (this condition will be similar to the EXW purchase condition). However, if there is an agreement to deliver goods to an intermediate location, the seller will have to bear the costs and risks of transportation such as damaged goods, lost goods… until the goods are delivered to the shipping unit. shipping specified by the buyer. In addition, the seller will not be responsible for unloading the goods from his means of transport.
There are 3 locations where deliveries can take place here. The buyer and seller must specify where exactly the transfer of risk will take place.
At the seller’s facility (factory), including loading onto collection vehicles
At the freight forwarding facility (cargo agent)
At the airport cargo terminal, including unloading from the delivery vehicle
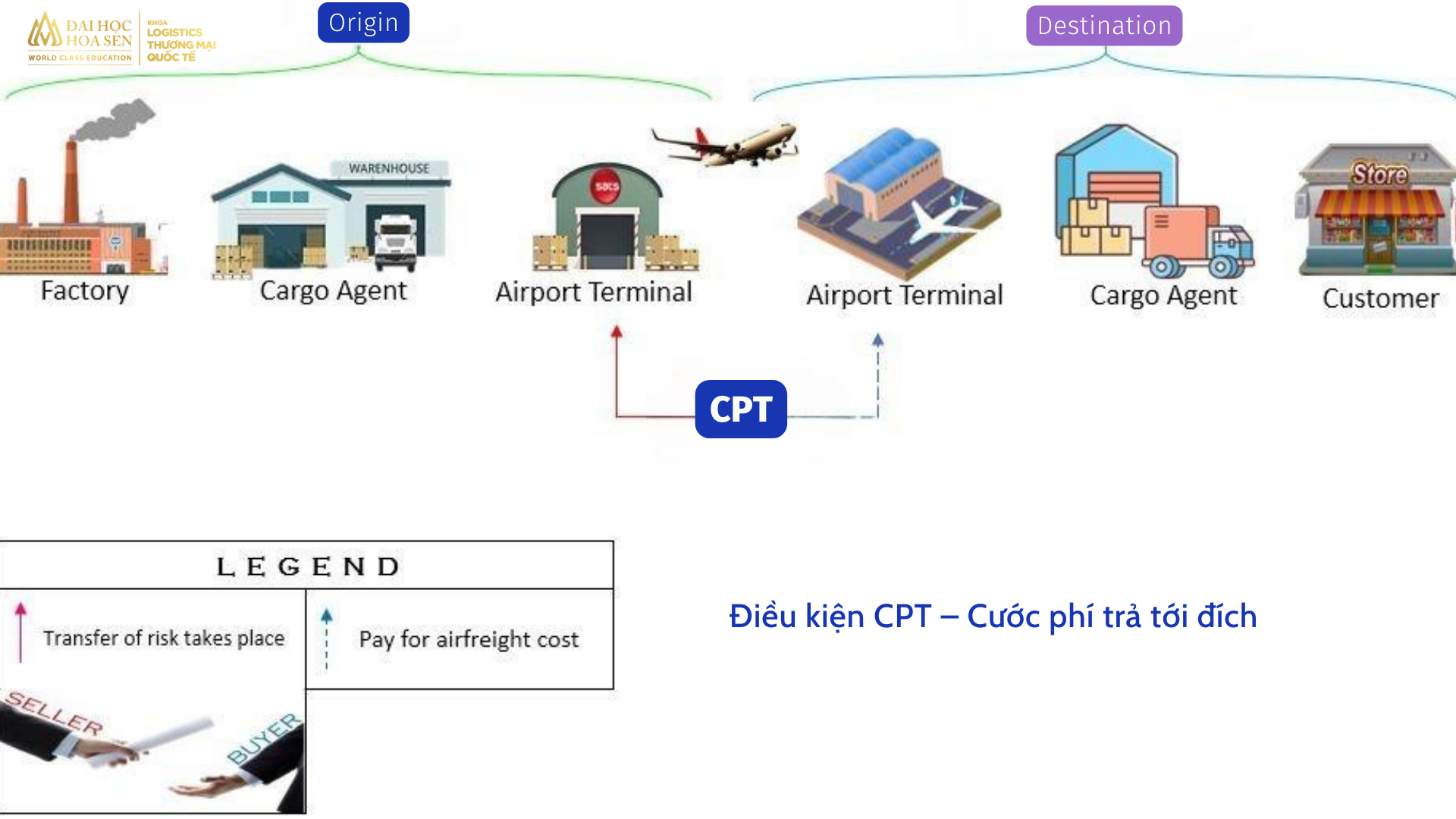
CPT terms – Freight paid to destination
CPT terms are often applied to multimodal transport, but are most commonly used for shipments by air. Accordingly, the seller will reserve a seat on the plane, bring the goods to the airport and complete related procedures before bringing the goods on the plane. All charges incurred until the goods arrive at the destination port will be paid by the seller.
The buyer will carry out import and export procedures and transport goods from the destination port to their warehouse or store. All costs during this period will be paid by the buyer. At the same time, from the time of receiving the goods at the destination port, all risks will transfer to the buyer. Therefore, to minimize damage to themselves, buyers should buy additional cargo insurance.
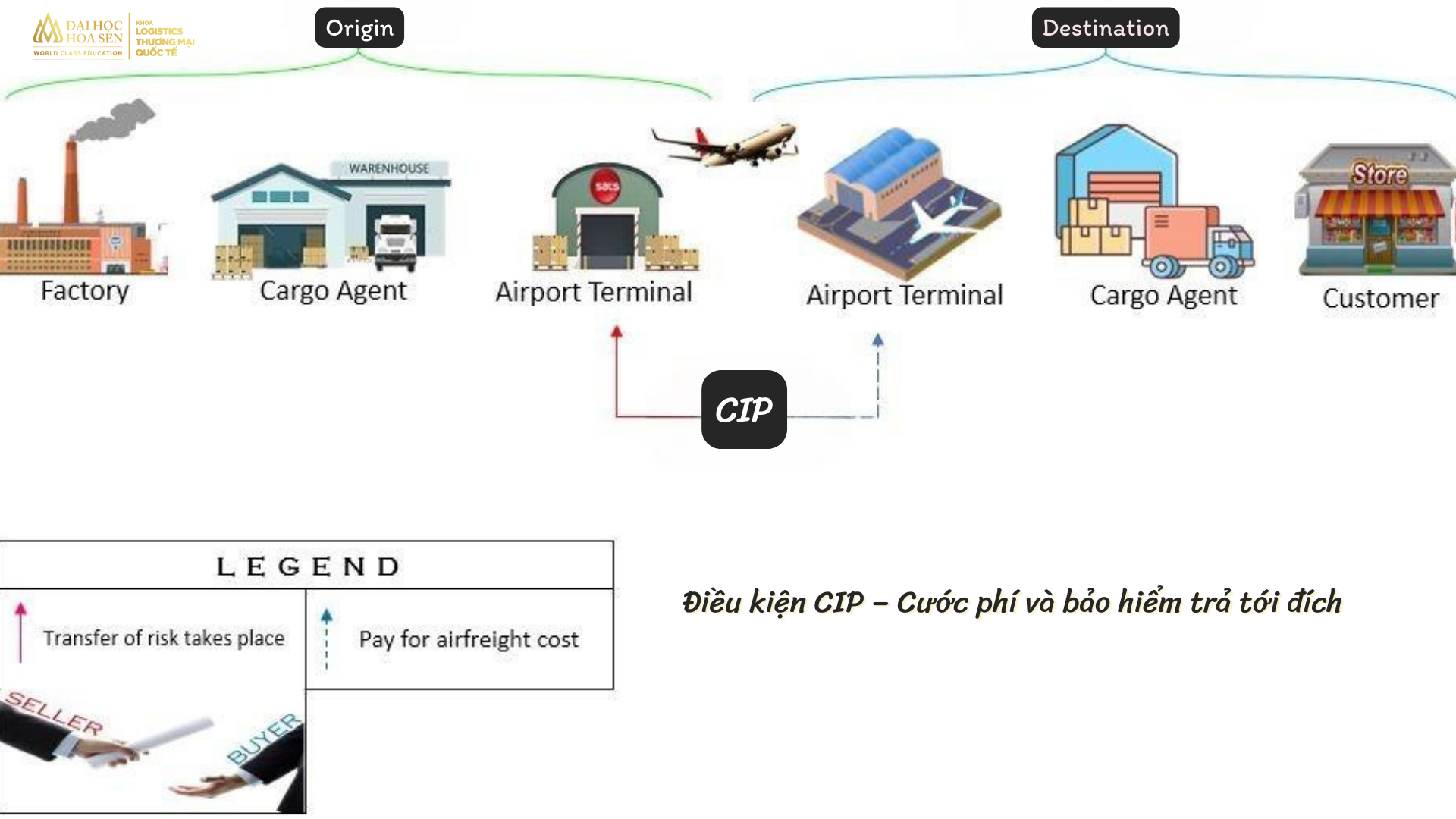
CIP Terms – Freight and insurance paid to destination
The CIP term adds an additional insurance responsibility on the seller’s part. However, the risk of loss passes to the buyer when the goods are loaded onto the plane. Other tasks such as booking seats on the plane, transferring goods to the plane, and paying freight to the destination port all belong to the seller. The place for transferring goods risk in CIP is at the export goods terminal. The seller fulfills his obligations regarding the goods when he has delivered them safely at the port of export cargo terminal.
Group D conditions (DAT- DAP- DDP)
Group D conditions (DAT- DAP- DDP) are most used in the process of importing and exporting goods by air. Group D conditions will include 3 conditions: DAT (delivery at terminal), DAP (delivery at destination), DDP (delivery with tax paid or delivery with import and export customs clearance). The final destination for receiving goods is the airport, cargo terminal or specified destination. In particular, the specified destination may be a warehouse or warehouse not located at the airport or International Intermodal Terminal.
Join:
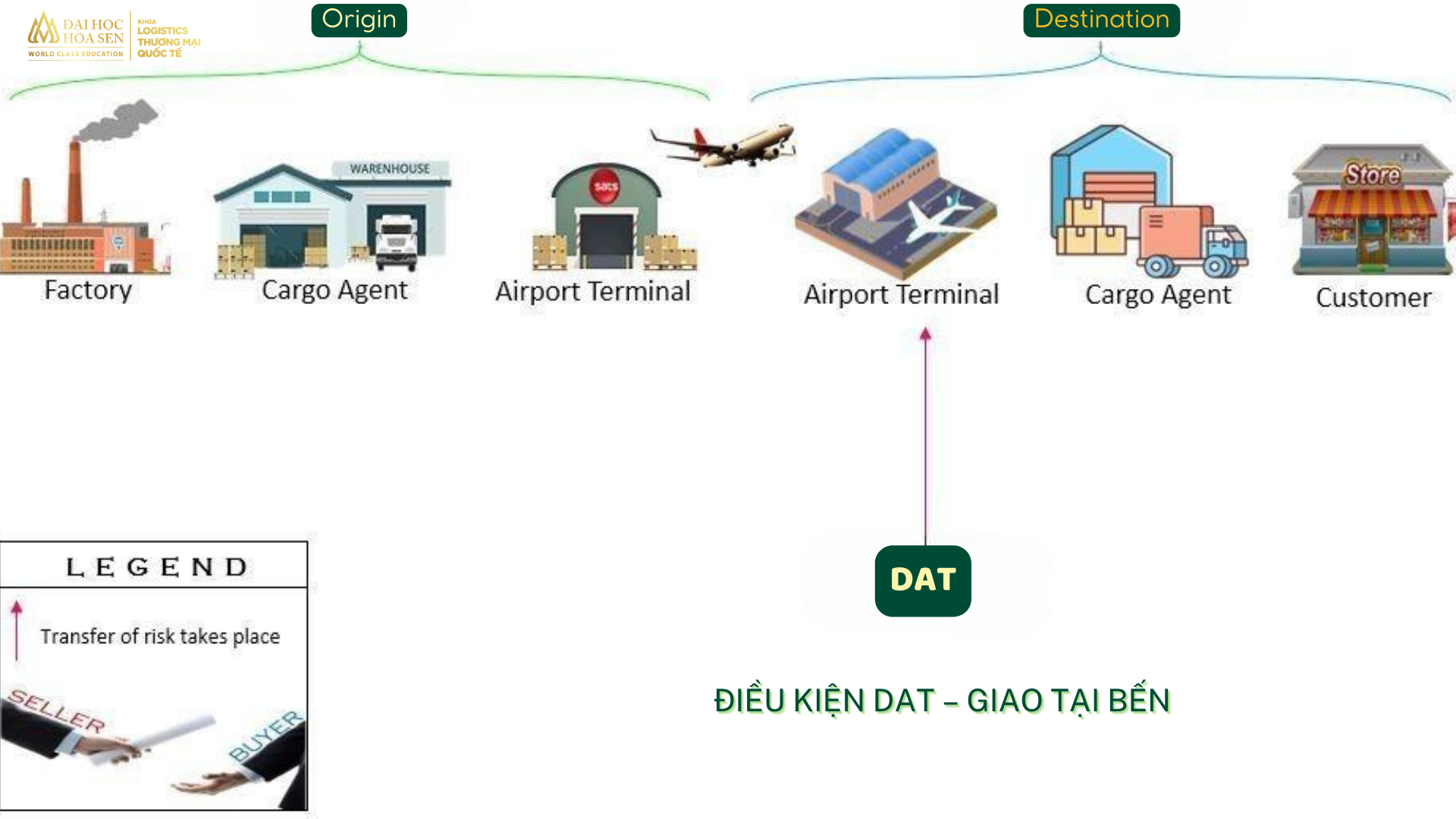
DAT conditions – Delivered at terminal
DAT conditions will clearly distinguish between costs and risks of the seller and the buyer. Accordingly, the seller will be the one to bear all shipping costs, insurance and risks before the goods are delivered to the destination port. The seller will bear all risks from unloading the goods from the aircraft, cargo terminal and transporting them to the buyer’s warehouse or store.
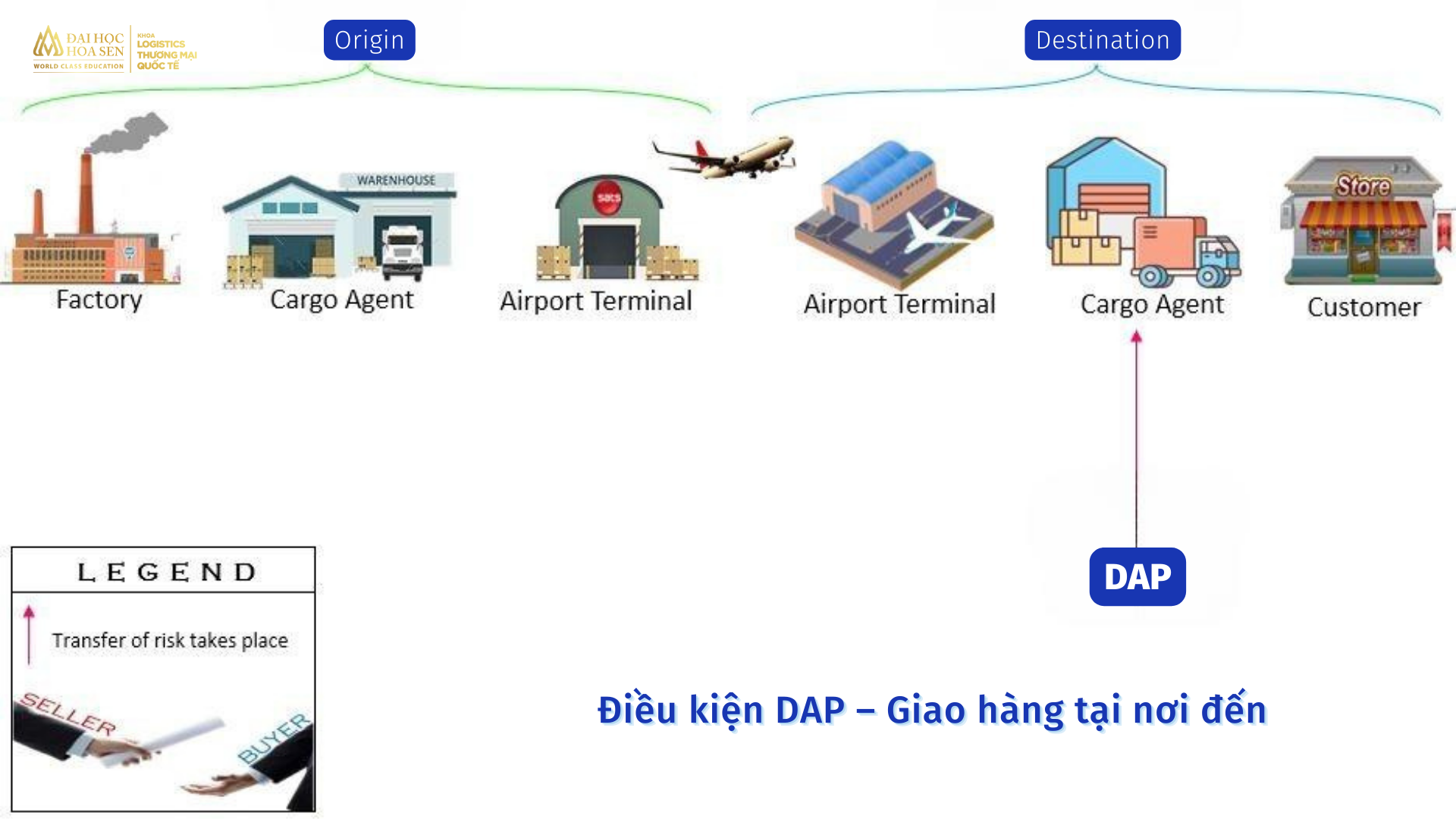
DAP conditions – Delivery at destination
In this condition, the seller will bear all costs and risks when the goods arrive at the specified destination. The transfer of risk in the goods takes place when the aircraft arrives at the destination airport and the goods have been removed from the aircraft. The seller is not responsible for customs clearance of imported goods from the airport terminal. This means that all work and risks will be the responsibility of the buyer.
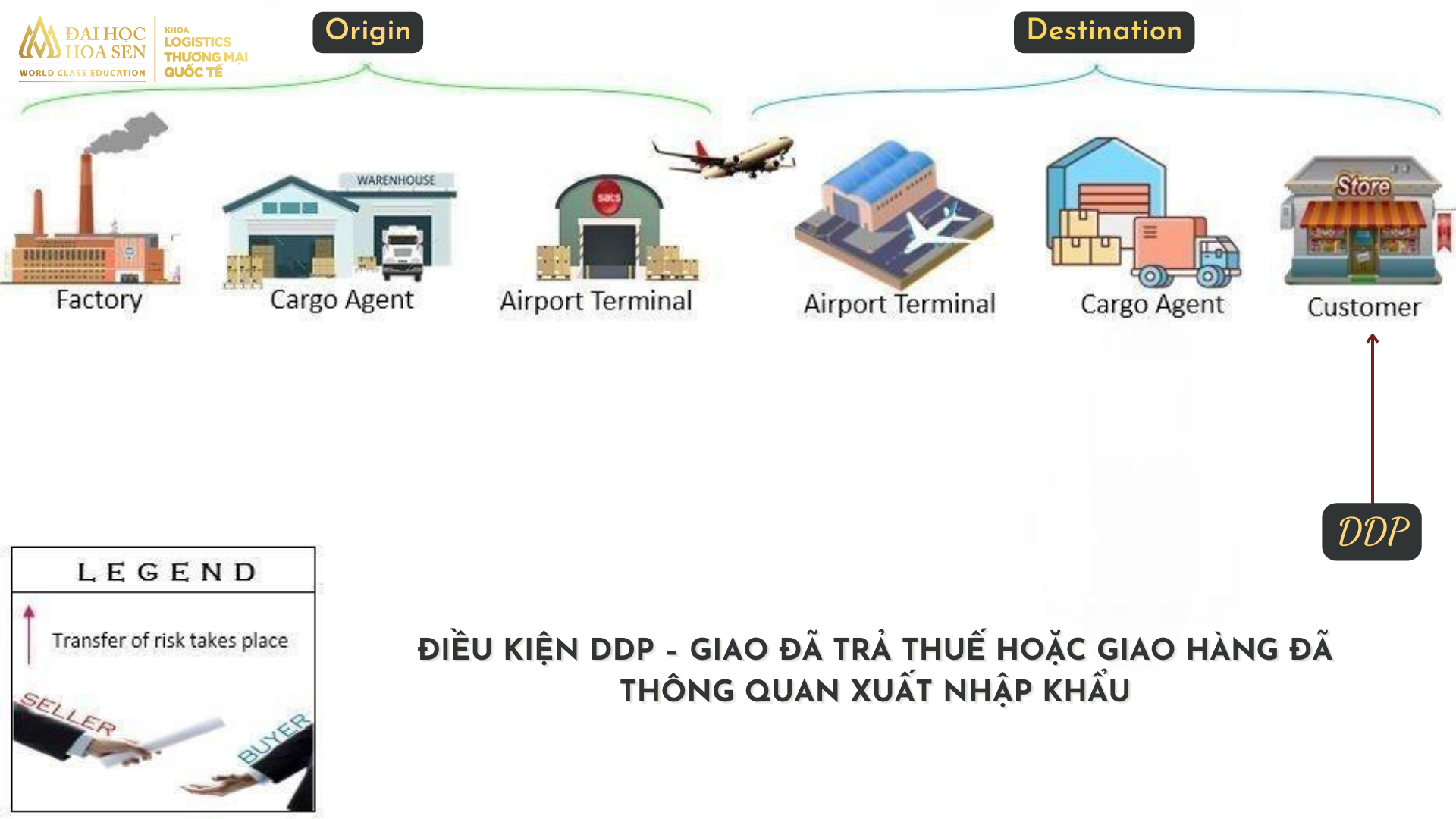
DDP conditions – Delivered with tax paid or Delivered with import and export customs clearance
Under the DDP condition, the seller will be the one to arrange the goods to be shipped to the destination of the buyer’s designated place. Besides, the seller will also carry out customs clearance procedures, buy insurance, take responsibility for risks or pay import and export taxes. The buyer is responsible for unloading the goods from the means of transport to their warehouse.
The content about DDP conditions has also ended this article. Faculty of Logistics – International Trade hopes that the above article will provide you with useful information about Incoterms conditions when importing and exporting by air and choosing the most suitable Incoterms conditions for freight shipments. not at the enterprise.